Knee joint replacement surgery in patient with Primary Lymphedema Stage III (ISL)
With thanks to María Del Rosario Pineda
About DEEP OSCILLATION®
DEEP OSCILLATION® is an internationally patented, proven technology based on the effects of creating an electrostatic field in the tissue of the patient. Easy application is from therapist to client via hygienic, vinyl gloved hands; utilizing all normal massage movements or via circular movements over the tissue with a handheld applicator. The handheld applicator also enables self-treatment.

The special structure of DEEP OSCILLATION® allows the creation of biologically effective oscillations in the treated tissue using electrostatic attraction and friction. In contrast to other therapies, these pleasant oscillations have a gentle and deep-acting effect on all tissue components to an 8 cm depth (through skin, connective tissue, subcutaneous fat, muscles, blood and lymph vessels.
Because of the non-invasive, non-traumatic, gentle nature of this therapy, very early possibilities of application are possible following injury and from Day One post operatively. Chronic conditions can also be worked upon with effective results.
The following physiological effects of DEEP OSCILLATION® are clinically proven:
- Highly effective in reducing pain
- Anti-inflammatory
- Effective in reabsorbing oedema (swelling)
- Encouraging wounds to heal
- Fibrosis Reduction
- Improving trophicity
- Rubor reduction (haematoma/bruising)
- Detoxification
- Improving quality of tissue
Learn more about DEEP OSCILLATION® biological and clinical effects
See all Deep Oscillation References
About Magcell

MAGCELL® is a portable hand device for electrode-free electrotherapy. Magnetic alternating fields are produced over rotation by permanent magnets. A sinusoidal pulsating electromagnetic field (PEMF) is generated over the special magnet arrangement and device function principle.
Clinical Effects
The following effects of electrode-free electrotherapy with MAGCELL® are clinically recorded:
- Pain alleviation and movement stimulation
e.g. in the case of osteoarthritis - Substantial improvement in circulation
- Reduction of sensory neurotoxicities (polyneuropathy)
- Recently studies showed a very good result by BPH
In blood flow stimulation (Source: Funk et al (2014)
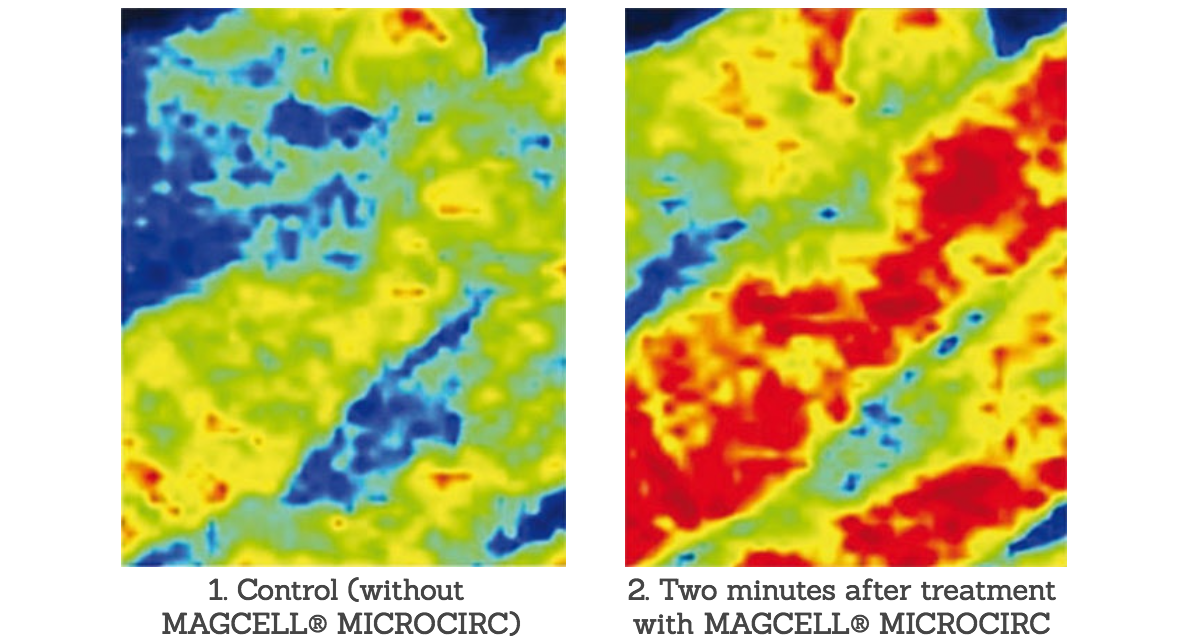
MAGCELL® MICROCIRC significantly increases micro-circulation (p < 0,001) while nitric oxide (NO) has a blood vessel dilatory effect. The authors recommend the therapy for clinical situations where an improvement in micro circulation is identified, like for instance in the case of chronic tissue repair.
Magcell References
Funk HW, Knels L., Augstein A., Marquetant R., Dertinger HF (2014): Potent Stimulation of Blood Flow of Volunteers after Local Short-Term Treatment with Low-Frequency Magnetic Fields from a Novel Device. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2014. Article ID 543564, 9 pages. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/543564 .
Geiger G., Mikus E., Dertinger H., Rick O. (2015): Low frequency magnetic field therapy in patients with cytostatic-induced polyneuropathy: A phase II pilot study. Bioelectromagnetics 36 (3): 251-254. doi: 10.1002 / bem.21897.
Hitrov NA, Portnov VV (2008): MAGCELL® ARTHRO in the treatment of osteoarthritis in the knee joint. Naturopathy 3, 25-27.
Leoci R., Aiudi G., Silvestre F., Lissner E., Lacalandra GM (2014): Effect of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy on Prostate Volume and Vascularity in the Traetment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Pilot Study in a Canine Model. The Prostate 74: 1132-1141.
Reimschüssel A., Bodenburg P. (2009): Low-frequency electromagnetic fields. Successful in the therapy of myoarthritis of the temporomandibular joint. Naturopathy 5, 28.
Rick O., von Hehn U., Mikus E., Dertinger H., Geiger G. (2017): Magnetic Field Therapy in Patients With Cytostatics-Induced Polyneuropathy: A Prospective Randomized Placebo-Controlled Phase-III Study. Bioelectromagnetics 38 (2): 85-94 :. doi: 10.1002 / bem.22005.
Wuschech H., von Hehn U., Mikus E., Funk RH (2015): Effects of PEMF on patients with osteoarthritis: Results of a prospective, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Bioelectromagnetics 36 (8), 576-585.

