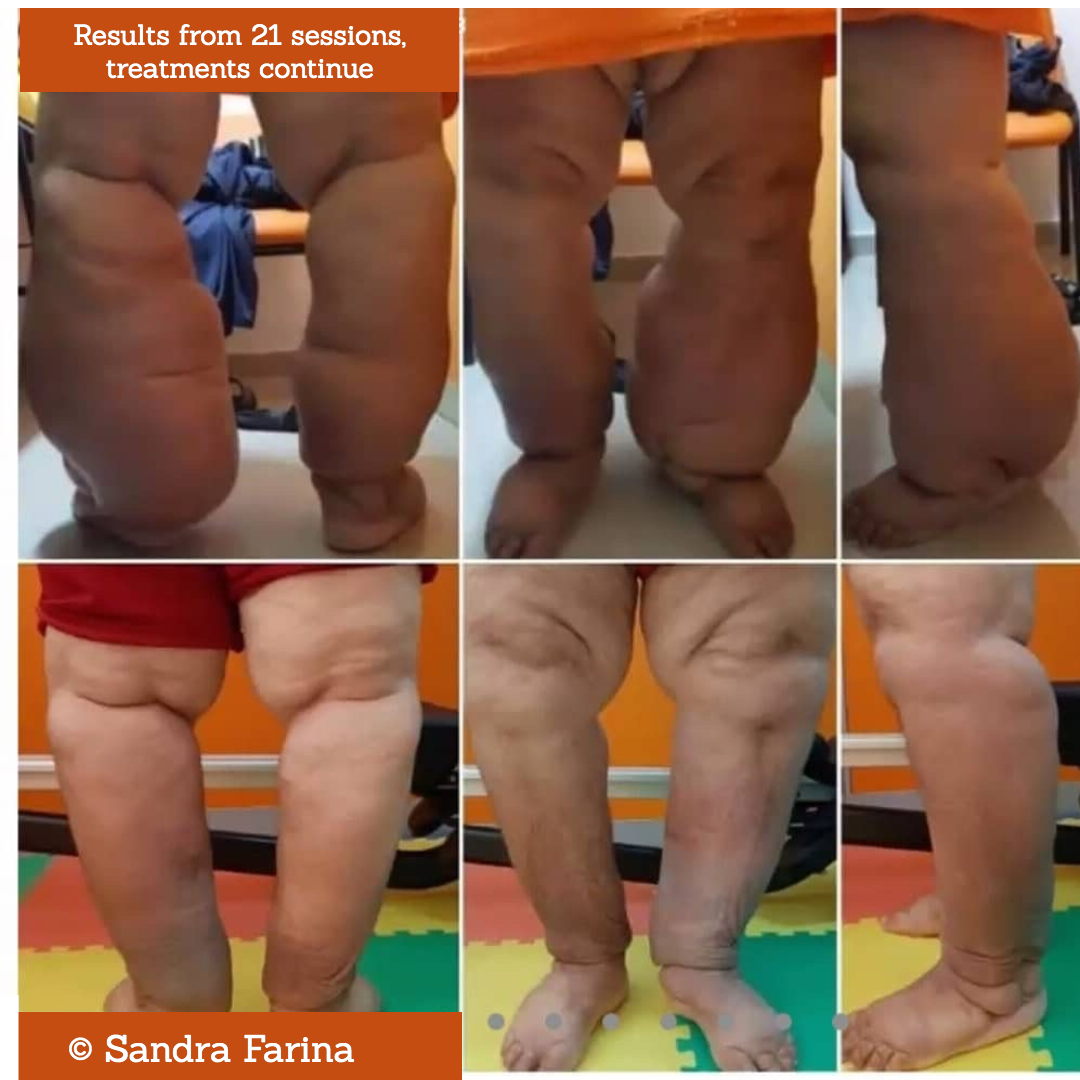
Bilateral Elephantiasis: Deep Oscillation Makes Positive Difference to Treatment Approach
A Case Report by Sandra Farina Kinesiologist, Peripheral Vascular Rehabilitator Coordinator and Spokesperson for Peripheral Vascular Rehabilitation for the ALCVA.
"After a lifetime of looking for help for his legs... we finally got to know each other and our treatment approach has made such a positive impact on this gentleman's quality of life.."
Background
The patient attended a kinesiology and physiotherapy consultation in peripheral vascular rehabilitation (thanks to a scholarship won through our rehabilitation unit). The patient, after what was discussed, the studies carried out previously and vascular kinesiological evaluation, was diagnosed with irreversible grade 3 Lymphoedema in both limbs with predominance in the left limb, reaching elephantiasis stage [1] and to a lesser extent in his right limb.
The patient reported that for as long as he can remember, his limbs have been swollen and getting worse every year. Some health professionals told him that there was no solution to his condition and that he had to learn to live with this problem... I want to clarify that although Lymphoedema cannot be cured when it is diagnosed, it is possible to have a better quality of life, as we demonstrated to our patient by means of our treatments.
Clinical Presentation
On further examination, it was seen that the patient has significant fibrosis in both extremities, more so in the right leg, and also bilaterally: interdigital mycosis, positive Stemmer's sign, positive Godet's Sign, marked folds, important lymphatic blockages which do not allow the lymphatic circulation to function properly. This has caused the Lymphoedema to continue to increase in size, complicating it further and resulting in repeated infections (cellulitis/erysipelas), both of which increase damage to the lymphatic system. The patient reports that he has had to be hospitalised on several occasions due to this. His gait was observed as altered when walking, which meant that the peripheral bellows (which ensure good circulatory return), cannot function correctly, further complicating the condition.
Measurements were taken and a therapeutic approach proposed which was appropriate to the condition and its stage.
Treatment Protocol
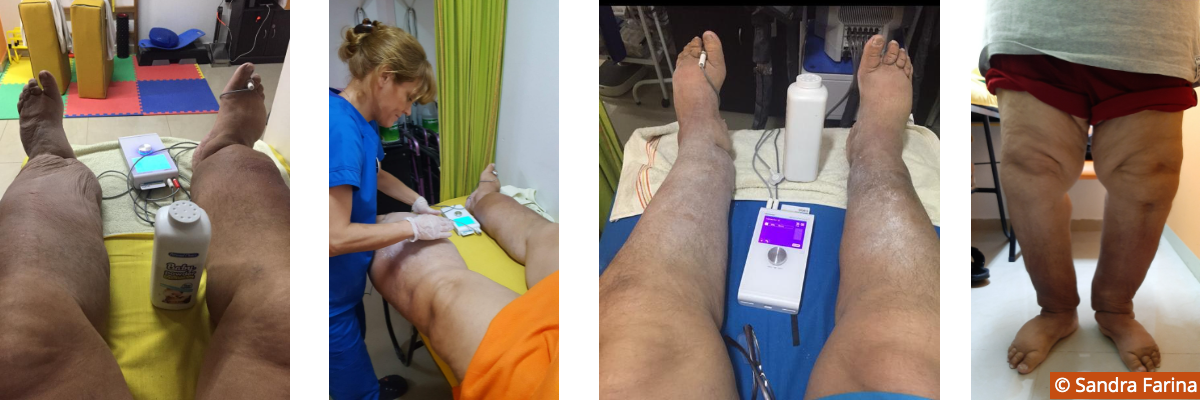
- A combination of Vodder Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD) and Deep Oscillation electrostatic therapy [2,3] were applied through gloved hands in order to reduce fibrosis. Combining these techniques achieves a stronger therapeutic effect.
- Sequential Pressure Therapy not exceeding 30 mmHg so as not to increase infiltration in the interstitial space.
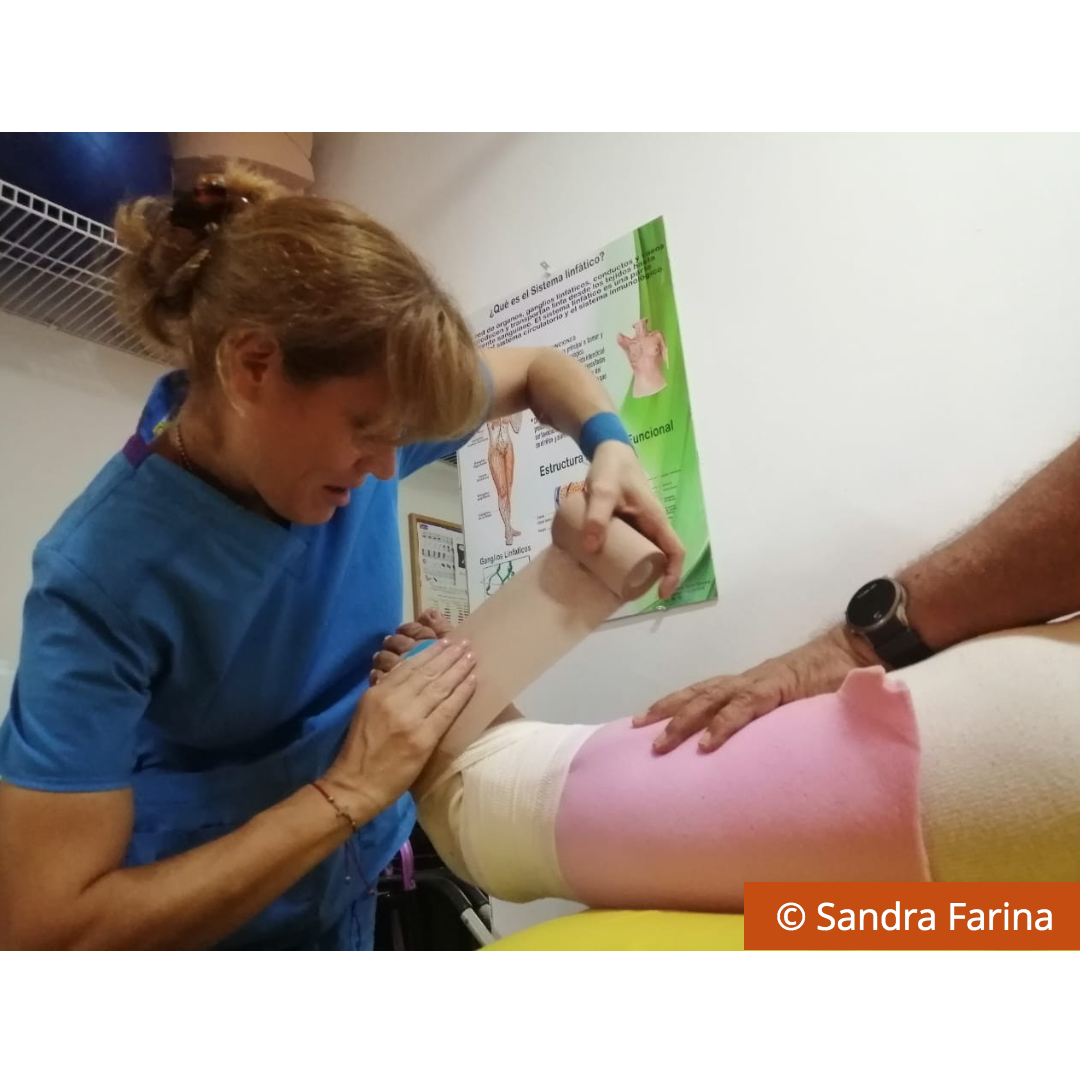
- Multilayer bandaging: 90 metres of bandages on the left limb and about 70 metres on the right
- Passive and active myolymphokinetic exercises (third pillar) and recommendations are given.
Treatment Regularity
The therapies are indicated to be carried out 3 times a week due to the type of lymphatic blockage that the patient presents and considering that lymphoedema cannot be cured, it is a pathology that can be controlled to improve the patient's quality of life and to avoid the complications of repeated infections.
Results
Since commencement of therapy, the patient has progressed in a most favourable way, highlighting the effectiveness of this therapeutic approach. This was one of the first cases with elephantiasis to be treated from the outset with Deep Oscillation. After 21 treatments we have achieved a result with more than 90% improvement, the patient continues to show good acceptance and we continue to evolve favourably.
Practitioner Conclusion
On a personal level, after being in contact permanently and every day with my patients, I had not previously observed the difference of approaching these cases with Deep Oscillation from the outset. I enjoy the electrostatic vibrations of Deep Oscillation that pass (intermittently) through my gloved hands whilst applying manual lymphatic drainage; utilising both tools definitely achieves more favourable outcomes.
It is important that the patient continues to attend therapy three times a week, as this is what the degree of Lymphoedema in both extremities’ merits. This way, a favourable course of treatment can be continued and the patient will not be put at risk again.
Current treatment protocol consists of Vodder MLD, Deep Oscillation, Sequential Pressure Therapy, Multilayer Taping alternating with compression stockings, active passive myolymphokinetic exercises and recommendations.
- It is important to note that MLD should always be performed by a specialist Practitioner, it is one of the key pillars in the therapeutic approach for a patient with Lymphoedema


1. Lymphatic filariasis (commonly known as Elephantiasis)
Key facts
- Lymphatic filariasis impairs the lymphatic system and can lead to the abnormal enlargement of body parts, causing pain, severe disability and social stigma.
- 859 million people in 50 countries worldwide remain threatened by lymphatic filariasis and require preventive chemotherapy to stop the spread of this parasitic infection.
- Lymphatic filariasis can be eliminated by stopping the spread of infection through preventive chemotherapy with safe medicine combinations repeated annually. More than 7.7 billion treatments have been delivered to stop the spread of infection since 2000.
- 51 million people were infected as of 2018, a 74% decline since the start of WHO’s Global Programme to Eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis in 2000.
- 648 million people no longer require preventive chemotherapy due to successful implementation of WHO strategies.
- An essential, recommended package of care can alleviate suffering and prevent further disability among people living with disease caused by lymphatic filariasis.
2. DEEP OSCILLATION®
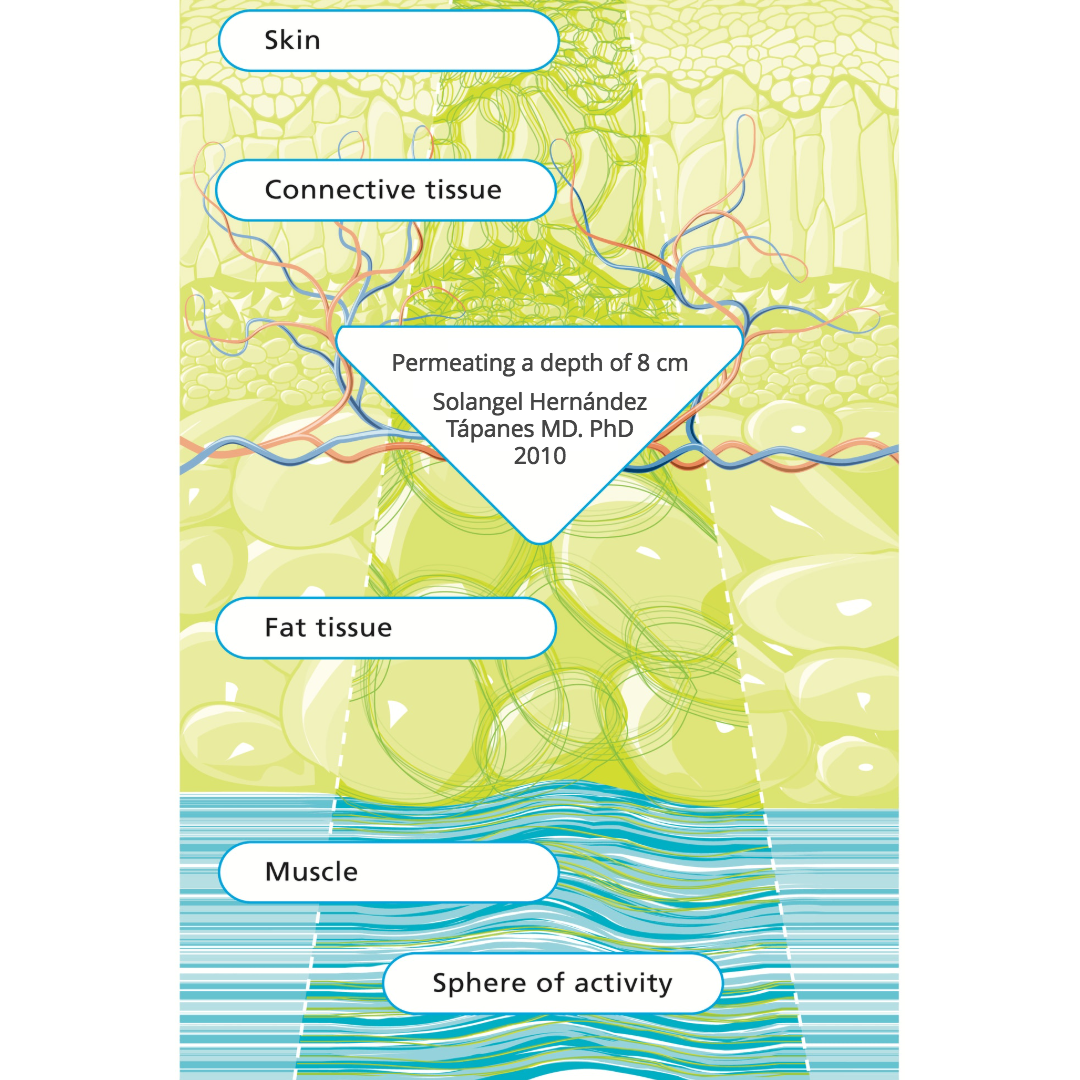
In contrast to externally applied, mechanical forms of therapy, (e.g. vibration), the therapy effect of DEEP OSCILLATION® takes place in the tissue itself and works through the entire depth of the tissue layers (skin, connective tissue, subcutaneous fat, muscles, blood and lymph vessels)
DEEP OSCILLATION® helps in speeding up and improving wound healing processes. Through the oedema-reducing and anti inflammatory effect, the local metabolic elimination and alimentation is improved in all tissue layers, whereby tissue regeneration and wound closure are encouraged on many levels. This is documented by the significant improvement in planimetric and biochemical parameters of the wound healing.
Because of the non-invasive, non-traumatic, gentle nature of this therapy, very early possibilities of application are possible following injury and from Day One post operatively. Chronic conditions can also be worked upon with effective results.
Learn more about DEEP OSCILLATION® biological and clinical effects
3. DEEP OSCILLATION references in Lymphoedema
Brenke R. - Therapie des Lymphödems EHK 2021; 70: 138-144 DOI - 10.1055/a-1477-817
Jui Chu Y. (2017): HIVAMAT 200. In: Jui Chu Y. (Ed.): What Can Physical Therapy Do After Breast Cancer Surgery. CARE, 187-188. German translation: What can physical therapy do after breast cancer surgery.
Kraus R. (2014): Intensive lymphatic drainage through deep oscillation. LYMPH & Health 2, 6-8.